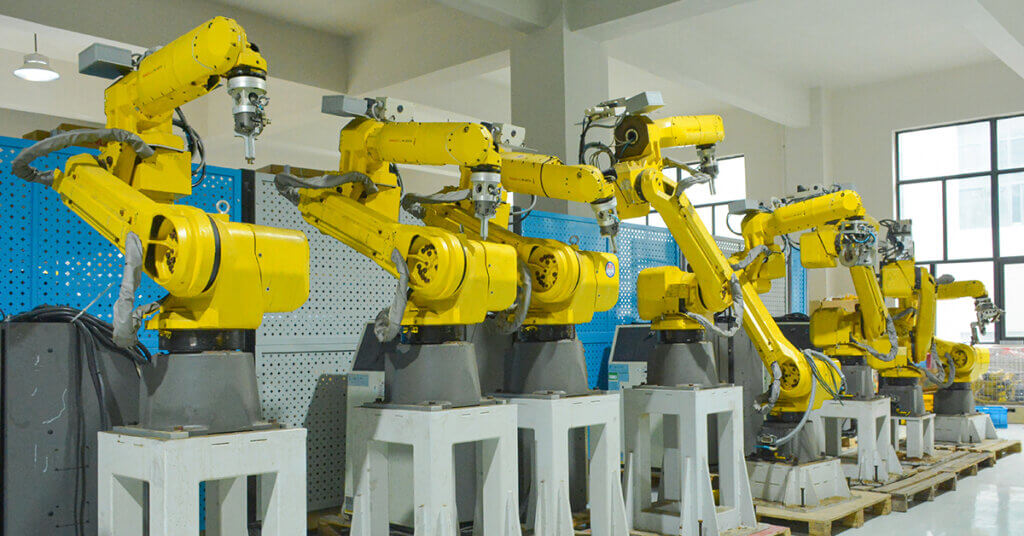
In the world of modern manufacturing, automation is essential for speed, precision, and productivity. One of the core components behind this automation revolution is the industrial motor. These motors power everything from robotic arms to CNC machinery, enabling factories to operate around the clock with incredible accuracy. In this article, we’ll explore the types of motors used in manufacturing automation, focusing on servo motors, linear motors, and spindle motors。
Introduction to Servo Motors
Servo motors are a backbone of automation systems. Unlike traditional motors that simply spin, servo motors are capable of precise control over position, speed, and torque. This makes them ideal for applications that require accurate movements, such as robotic assembly, conveyor systems, and automated inspection machines.
Here are the current functions of each loop:
- Position control loop – commands the velocity control loop in order to ensure the motor is rotating into the correct position.
- Velocity control loop – controls the velocity (the amount of rotational velocity of the motor shaft) of the motor.
- Current control loop – prevents the motor from being overloaded by controlling the current of the motor.
A servo motor works with a feedback mechanism, often using an encoder, to constantly adjust its output. This feedback loop allows it to correct its position in real time—essential in environments where even a millimeter of deviation can result in faulty production.
Reviewing The Five Major Servo Motor Types
In total, there are five main varieties of servo motors. Application, operating environment, and cost are three prominent factors when deciding on which specific servomechanism to use.
- AC Servo Motors: These are widely used in manufacturing due to their high efficiency and performance. They are well-suited for applications requiring high speed and torque control.
- DC Servo Motors: Though less common in modern factories, DC servo motors offer simple control and are still used in specific low-power or cost-sensitive scenarios.
- Positional Rotation Servo Motor: The positional rotation servo motor is one of the most widely used in automation systems today. Its output shaft typically rotates within a fixed arc—usually up to 180°—making it ideal for applications requiring limited angular movement. Built-in mechanical stops prevent over-rotation, protecting the internal sensors and components. You’ll find these motors in everything from robotic grippers to smart cameras and educational kits where precise angle control is essential.
- Continuous Rotation Servo Motor: Unlike its positional counterpart, the continuous rotation servo motor isn’t limited to a set angle. Instead, it can spin in either direction indefinitely, functioning more like a traditional DC motor but with enhanced control features. Input signals determine both the direction and speed of rotation, making it perfect for mobile platforms, robotic wheels, and automated conveyor systems that require fluid, ongoing motion.
- Linear Servo Motor: A linear servo motor doesn’t rotate at all—instead, it translates electrical energy directly into straight-line motion. By using either a magnetic or gear-driven system, it eliminates the need for rotary-to-linear conversion components, increasing speed and efficiency. Linear servos are commonly found in pick-and-place robots, medical imaging equipment, and precision CNC machines, where accurate and rapid linear travel is essential for high-quality performance.
Fanuc brand motors
Spindle Motors in Manufacturing Automation
Spindle motors are essential components in modern manufacturing, especially in high-speed and high-precision machining tasks such as milling, grinding, drilling, and cutting. Designed to operate at high RPMs, these motors enable rapid acceleration and deceleration—ideal for applications that demand fast start-stop motion and 360° positioning.
Unlike typical servo motors, spindle motors can run on open or closed-loop systems, and while they don’t always require feedback devices like encoders or resolvers, they can be equipped with positional sensors or tachometers for enhanced control. This flexibility allows them to balance power efficiency and precision, depending on the application.
To maintain consistent performance at varying speeds, spindle motors are typically built with advanced cooling systems and vibration-suppression features, ensuring accuracy and durability even under continuous, high-load conditions. You’ll find them in CNC machines working on metal, wood, stone, glass, and even PVC materials—industries where surface quality and dimensional tolerances are non-negotiable.
Now that you’ve got a better understanding of how different motors function in automation, feel free to explore our motor catalog to find the right fit for your application. Not sure which motor suits your setup? Contact CIT Automation Equipment’s technical support team—we’re here to guide you step by step in selecting the correct part. Have an existing system that needs attention? We also offer repair services for industrial servo and spindle motors to get you back up and running fast.